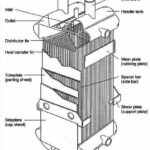
What is a Coalescer?
So What is a Coalescer? They are a type of filtration equipment used to separate immiscible liquids, such as oil and water. The basic principle of coalescence is that small droplets of one liquid will combine or “coalesce” into larger droplets, which can then be more easily separated from the main stream. So they work by promoting the coalescence of small droplets into larger ones, which are then easier to separate.
Coalescers typically consist of a filter medium, such as a mat of fibres or a bed of beads, that provides a large surface area for the droplets to come into contact with. The droplets are then removed from the main stream by gravity, pressure, or a combination of both.
Coalescers are commonly used in a variety of industries, including oil and gas, wastewater treatment, and chemical processing. They are used to remove water or other contaminants from fuels, to separate oil from produced water in oil and gas production, and to remove oil from wastewater in industrial processes.
Types
There are different types, but some of the most common ones include:
- Mesh Type: These are made of layers of fine mesh, which trap liquid droplets as the gas stream passes through. They work by creating a tortuous path for the gas, which causes the droplets to collide and stick to the mesh.
- Fiberbed Type: These consist of layers of fibers that are designed to trap liquid droplets. As the gas passes through the fiber bed, the droplets stick to the fibers and coalesce into larger droplets, which are then removed from the gas stream.
- Cyclone Type: These use centrifugal force to separate liquid droplets from a gas stream. The gas is spun around in a cyclone chamber, causing the droplets to move to the outside of the chamber where they can be removed.
- Electrostatic Type are another type of coalescer. They work by applying an electric field to the gas-liquid mixture, which causes the droplets to become charged. The charged droplets are then attracted to a collecting surface with the opposite charge, where they coalesce into larger droplets that can be removed from the gas stream. Electrostatic coalescers are particularly effective at separating small droplets from a gas stream and can achieve high separation efficiency. They are commonly used in the petroleum and chemical industries to remove water and other liquid contaminants from natural gas, crude oil, and other process streams. Electrostatic coalescers can also be used in the power generation industry to remove fine particles from flue gas streams, which can help to reduce emissions and improve air quality. They are often used in conjunction with other types of pollution control equipment, such as scrubbers and baghouses, to achieve more comprehensive particulate removal.
- Plate Type: These are similar to mesh coalescers but use a series of parallel plates instead of mesh layers. The plates are arranged at an angle to the gas flow, which causes the droplets to coalesce and drain off the plates. Plate coalescers are often used in industrial applications to remove liquid contaminants from gas streams.
- Centrifugal Type: These are similar to cyclone coalescers but use a rotating drum or disk instead of a fixed cyclone chamber. The gas-liquid mixture is fed into the drum, and the centrifugal force separates the liquid droplets from the gas stream. Centrifugal coalescers are often used in oil and gas production to separate water and other liquids from natural gas.
- Membrane Type: These use a porous membrane to remove liquid droplets from a gas stream. The membrane has a hydrophobic surface that repels the liquid droplets, causing them to coalesce and form larger droplets that can be removed from the gas stream. Membrane coalescers are often used in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries to remove liquid contaminants from process gases.
- Foam Type: These are used to separate liquids from foams. The foam is fed into a chamber where it comes into contact with a liquid that is immiscible with the foam. The liquid drains out of the foam, causing the bubbles to collapse and the liquid droplets to coalesce. Foam coalescers are often used in the food and beverage industry to separate liquids from foams, such as in the production of beer and other carbonated beverages.
- Gravity Type: These use gravity to separate liquid droplets from a gas stream. The gas-liquid mixture is fed into a vessel, where the liquid droplets settle to the bottom due to their higher density. The clean gas is then removed from the top of the vessel. Gravity coalescers are simple and easy to operate, but they are less efficient than other types of coalescers and require a large amount of space.
- Vane pack Type: These consist of a series of vanes arranged in a pack that is inserted into a gas stream. The vanes cause the gas to change direction, which promotes the coalescence of liquid droplets. The liquid droplets coalesce on the vanes and drain off into a collection chamber. Vane pack coalescers are often used in the oil and gas industry to remove water and other liquid contaminants from natural gas.
- Ultrasonic Type: These use high-frequency sound waves to promote the coalescence of liquid droplets. The sound waves cause the droplets to collide and stick together, forming larger droplets that can be removed from the gas stream. Ultrasonic coalescers are often used in laboratory and research applications, such as in the production of pharmaceuticals and other chemicals.
- Packed bed Type: These use a bed of randomly packed media, such as ceramic or metal balls or plastic packing, to separate liquid droplets from a gas stream. The media provides a large surface area for the droplets to coalesce, and the resulting larger droplets can be removed from the gas stream by gravity or by draining off the bottom of the bed. Packed bed coalescers are commonly used in chemical and petrochemical processes, as well as in the oil and gas industry, to remove liquid contaminants from gas streams. Packed bed coalescers are effective for applications where the droplets are relatively large and where there is a high concentration of liquid. They are also useful for handling large gas volumes and can achieve high separation efficiency. However, they can be more difficult to clean than other types of coalescers, and they may require frequent replacement of the packing material.
Packed bed type are effective for applications where the droplets are relatively large and where there is a high concentration of liquid. They are also useful for handling large gas volumes and can achieve high separation efficiency. However, they can be more difficult to clean than other types of coalescers, and they may require frequent replacement of the packing material.
Each type of coalescer has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of coalescer depends on the specific application and process requirements. Factors to consider include the size and concentration of the liquid droplets, the flow rate and pressure of the gas stream, and the type of liquid and gas being processed.

These are the main types of coalescers used in industrial and laboratory applications. However, there may be variations or combinations of these types that are used in specific applications or for specialized processes.
It’s worth noting that the selection of a coalescer is highly dependent on the specific application and the characteristics of the gas and liquid being processed. Factors such as flow rate, pressure, droplet size and concentration, and the chemical and physical properties of the gas and liquid all need to be considered in selecting the appropriate type of coalescer.
Examples of liquid coalescers include the use of mesh or fiberbed type in the petroleum industry to remove water droplets from crude oil. These coalescers are used in various stages of the refining process, including the desalter, which removes salt and water from the crude oil, and the dehydrator, which removes water from the refined products.
Examples of gas coalescers include the use of fiberbed or cyclone type in natural gas processing plants to remove liquid droplets from the gas stream. These coalescers are used to prevent damage to downstream equipment, such as compressors and turbines, and to improve the quality of the natural gas.
Coalescer advantages and disadvantages
Below are some general advantages and disadvantages of using coalescers for liquid-liquid separation include:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| High efficiency: Coalescers are capable of removing small droplets of one liquid from another with high efficiency, achieving a separation of 99% or higher. | Limited applicability: they are not suitable for all types of liquids, and their effectiveness can be limited by the viscosity, density, and other physical properties of the liquids being separated. |
| Easy maintenance: Coalescers are relatively simple and straightforward to maintain, with regular cleaning and replacement of filter media as necessary. | High pressure drop: they can result in a high pressure drop across the filter, which can increase energy consumption and reduce efficiency. |
| Versatility: Coalescers can be used in a variety of applications and can handle a wide range of fluid temperatures, pressures, and flow rates. | Clogging: Coalescers can become clogged with debris, reducing their effectiveness over time. |
Summary
Coalescers are a versatile and effective option for separating immiscible liquids, but the limited applicability, high pressure drop, and potential for clogging must be considered when making a decision.