This short article discuss what are evaporators and looks briefly in their different types. The article also looks at the advantages and disadvantages of evaporators.
What are evaporators?
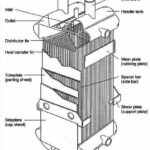
What are evaporators? An evaporator is a device used to separate a liquid from a solution by boiling off the liquid and leaving behind the solid components. This is accomplished by applying heat to the solution, causing the liquid component to vaporize and separate from the solid components.
Evaporators are used in a variety of industries, including food and beverage processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical processing. They are commonly used to concentrate solutions, remove water, and separate components of a mixture.
Type of evaporators
There are several types of evaporators, including:
- Forced Circulation Evaporators: These evaporators use a pump to circulate the solution and ensure uniform heating and evaporation. This type of evaporator is commonly used in high-volume industrial applications.
- Natural Circulation Evaporators: In these evaporators, the solution is heated and the resulting vapor rises, causing circulation of the solution. This type of evaporator is commonly used in low-volume applications.
- Falling Film Evaporators: In these evaporators, a thin film of the solution is allowed to flow down the heating surface, where it is rapidly evaporated. This type of evaporator is commonly used for heat-sensitive solutions, as the short residence time of the solution minimizes degradation.
- Rising Film Evaporators: In these evaporators, the solution is heated and rises up the heating surface, where it is rapidly evaporated. This type of evaporator is commonly used for solutions with high viscosities, as the rising motion of the solution helps to reduce the viscosity and improve heat transfer.
Advantages and disadvantages of evaporators
After discussing what are evaporators we can now look at their advantages and disadvantages as shown in the table below:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Ability to concentrate solutions | Risk of fouling of the heating surface |
| Efficient separation of components | Risk of degradation of heat-sensitive components |
| Ability to remove water | Energy-intensive process |
| Reduced disposal costs for waste streams | Requirement for careful control of temperature and pressure to prevent over-concentration or boiling over of the solution. |