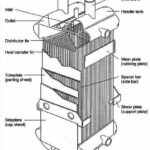
Cooling towers! this article will discuss their types, uses and applications in industry, will also look at advantages and disadvantages. Toch on a general sizing procedures.
What Are Cooling towers?
Cooling towers are large, specialized structures used to remove heat from water that has been used in industrial processes or air conditioning systems. The towers operate by allowing hot water to flow over a series of heat exchanger surfaces, which use evaporation to remove the heat and cool the water. The cooled water is then circulated back through the industrial process or air conditioning system.
Types of cooling towers
There are several different types of cooling towers, each with its own unique design and function:
- Natural Draft Cooling Towers: These are the largest and most common types of cooling towers, and they use natural convection to draw air through the tower. They are typically used in large industrial applications, such as power plants and petrochemical plants.
- Forced Draft Cooling Towers: These towers use fans to draw air through the tower, which increases their cooling efficiency. They are typically smaller than natural draft towers and are used in a variety of industrial and commercial applications.
- Induced Draft Cooling Towers: These towers use fans to draw air through the tower, but the fans are located at the top of the tower and pull air upward. This design is more efficient than forced draft towers, but they require more maintenance due to the location of the fans.
- Crossflow Cooling Towers: These towers have a unique design that allows the water and air to flow across each other at right angles. This design is more efficient than traditional cooling towers, but they are more expensive to construct and maintain.
Common process
Their uses and applications are vast, and they are typically used in industries that require large amounts of water to be cooled. Some of the most common applications include power generation, chemical processing, and HVAC systems.
Here are a few examples of processes that commonly them:
- Power Generation: Cooling towers are used in power plants to cool the water that has been used to condense steam back into liquid form after it has passed through a turbine. This process generates electricity, and the cooling tower helps to dissipate the heat that is created.
- Chemical Processing: Many chemical processes require water to be cooled as it passes through heat exchangers. Cooling towers are used to remove the heat and cool the water so that it can be reused in the process.
- HVAC Systems: Commercial and residential HVAC systems use cooling towers to remove heat from the water used to cool the air. The cooled water is then circulated back through the system to provide additional cooling.
- Food and Beverage Production: In food and beverage production, cooling towers are used to cool water that is used in various stages of the process, such as cooking, cleaning, and packaging.
- Oil Refineries: Cooling towers are used in oil refineries to cool the water that is used to cool the equipment and remove heat from the process. This helps to protect the equipment from damage and improve the efficiency of the refining process.
These are just a few examples of the many processes that use cooling towers. Any process that requires large amounts of water to be cooled can benefit from the use of a cooling tower.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of cooling towers include:
- Energy Efficiency: Cooling towers are more energy-efficient than other cooling systems, such as air conditioning, which can save companies money on energy costs.
- Water Conservation: By reusing water in industrial processes, cooling towers can help conserve water resources.
- Low Maintenance: Cooling towers require minimal maintenance, and they have a long service life.
Disadvantages of cooling towers include:
- Water Treatment: Cooling towers require regular water treatment to prevent bacteria growth and mineral build-up.
- Environmental Impact: Cooling towers can have a negative impact on the environment if they are not properly maintained or if they release contaminated water.
- Noise Pollution: Cooling towers can be noisy, which can be a problem in residential areas or near sensitive facilities.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Energy Efficient | Regular water treatment |
| Water Conservation | Can have negative environmental Impact |
| Low Maintenance | Noisy |
General Sizing Steps
Sizing a cooling tower involves determining the appropriate capacity of the tower to efficiently cool the water in a particular industrial process or air conditioning system. Here are the general steps to follow when sizing a cooling tower:
- Determine the Heat Load: The first step is to calculate the heat load, which is the amount of heat that needs to be removed from the water. This can be calculated by multiplying the flow rate of the water by the temperature difference between the inlet and outlet water.
- Determine the Water Flow Rate: The water flow rate is the amount of water that needs to be cooled. This can be calculated by dividing the heat load by the temperature difference and the specific heat of water.
- Select the Cooling Tower Type: Based on the specific requirements of the application, select the appropriate type of cooling tower. Consider factors such as the space available, the level of cooling required, and the desired efficiency.
- Determine the Tower Capacity: The capacity of the cooling tower is the amount of heat it can remove from the water. This can be calculated by dividing the heat load by the cooling range, which is the difference between the inlet and outlet water temperatures.
- Consider Other Factors: Additional factors to consider when sizing a cooling tower include ambient air temperature, relative humidity, and altitude. These factors can affect the tower’s performance and should be taken into account during the sizing process.
It is important to note that sizing a cooling tower is a complex process and should be done by a professional with experience in the field. There are also several online tools available that can help with the calculations, but they should be used as a general guide and not as a substitute for professional expertise.
External Links
Air cooled heat exchanger design – thermal design and sizing calculations for air cooled heat exchangers