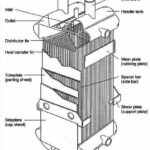
Definition
Compact heat exchanger can be characterized by its high ‘area density’ this means that is has a high ratio of heat transfer surface to heat exchanger volume. So Compact heat exchange is characterized by high heat transfer surface-area to volume ratios and high heat transfer coefficients compared to other exchanger types. A heat exchanger having a surface area density greater than about 700 m2/m3 for a gas is quite arbitrarily referred to as a compact heat exchanger. The heat transfer surface area is increased by fins to increase the surface area per unit volume and there are many variations available 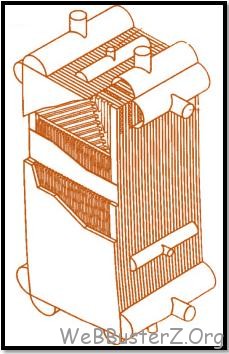
Compact heat exchangers are not a new technology there is a continuous need to produce innovative designs to suit market requirements. Such designs are more efficient in terms of heat transfer although fouling and pressure are important design considerations that make compact heat exchangers not suitable for all applications.
The threshold area/volume densities of a range of generic heat exchanger types that could all be classed as ‘compact’ are listed below:
| Compact heat exchanger operation type | Area/Volume ratio including fins |
|---|---|
| Gas-Gas | Greater than 500 m2/m3 |
| Gas Liquid | Greater than 500 m2/m3 |
| Liquid-Liquid | Greater than 200 m2/m3 |
Compact heat exchangers are commonly used for both single phase and two-phase applications
Compact Heat Exchanger Types
There are many types available from suppliers, below is a short list:
- Plate and Frame Heat Exchangers
- Brazed Plate Heat Exchangers
- Welded Plate Heat Exchanger
- Plate-Fin Heat Exchangers
- Brazed Plate-Fin Heat Exchangers
- Diffusion-Bonded Plate-Fin Heat Exchangers
- Spiral Heat Exchangers
- Printed Circuit Heat Exchangers
- Plate and Shell Heat Exchangers
- Polymer Heat Exchangers
Most common compact heat exchangers are plate-fin and tube-fin heat exchangers. Adding fins increases the heat transfer surface area of these types of heat exchangers.
Usage in process industry
Nowadays compact heat exchangers are widely used some examples are vehicular heat exchangers, condensers and evaporators in air-conditioning and refrigeration industry, aircraft oil coolers, automotive radiators, oil coolers, unit air heaters, intercoolers of compressors, and aircraft and space applications also used in cryogenics process, electronics, energy recovery, conservation and conversion
Types of Compact Heat Exchanger Typical Use in Each Process Industry
| Industry Application | Heat Exchanger Type |
|---|---|
| Food and drink |
|
| Chemicals and Petrochemicals |
|
| Oil and gas processing |
|
| Paper and board |
|
| Prime movers |
|
| Textiles and fabric care |
|
| Mechanical vapour recompression |
|
| District Heating/Cooling |
|
| Refrigeration |
|
| Air compressors |
|
| Cryogenics |
|
Advantages and Disadvantages
Below are some advantages of compact heat exchangers
- Lower capital cost and footprint, a compact heat exchanger can replace some normal size heat exchangers bringing advantages in performance.
- Energy efficient
- Wide variety of configurations to suit most processes heat transfer requirements
- Small size and volume
Below are some disadvantages
- Fouling can be an issue.
- Lack of user awareness as choice can also be limited to high pressure operation